Function Of Body Tube In Microscope
Espiral
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
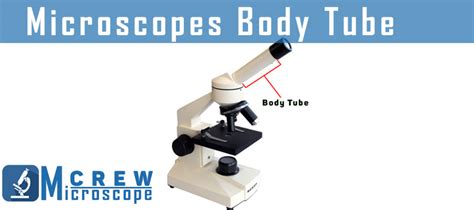
Table of Contents
The Unsung Hero of Microscopy: Understanding the Function of the Body Tube
The microscope, a marvel of engineering, allows us to peer into the intricate world of the microscopic. While the lenses grab most of the attention, a crucial, often overlooked component ensures the seamless transmission of light and the formation of a clear image: the body tube. Understanding its function is key to appreciating the overall performance and capabilities of any microscope. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the anatomy, function, and significance of the body tube in various microscope types.
What is a Microscope Body Tube?
The body tube, also known as the microscope barrel, is the cylindrical structure connecting the objective lens (near the specimen) to the eyepiece lens (near the observer's eye). It's essentially the optical pathway of the microscope, responsible for guiding the light from the objective lens to the eyepiece. Its seemingly simple design plays a critical role in image formation, magnification, and overall microscope functionality. Variations in length and design exist across different microscope types, influencing their optical properties and capabilities.
Key Features and Components:
- Length: The length of the body tube significantly impacts magnification. Different microscope types and manufacturers may have different standard lengths.
- Material: Typically made of sturdy metal (brass or steel) for durability and stability, but some modern microscopes incorporate lightweight materials.
- Internal Coating: The inner surface may be coated with a non-reflective material to minimize light loss and improve image clarity.
- Connections: It houses the precise connections for both the objective and eyepiece lenses, ensuring secure alignment and stable positioning.
- Internal Mechanisms (in certain models): Some advanced microscopes may integrate mechanisms within the body tube, like focusing adjustments or internal prisms for image manipulation.
The Crucial Role of the Body Tube in Image Formation
The body tube's primary function is to maintain the precise alignment of the optical components—the objective and eyepiece lenses—to create a clear, magnified image. Any misalignment or distortion within the tube directly affects image quality, introducing aberrations like blurring, distortion, or chromatic aberration.
The light path from the specimen to the eye follows this sequence:
- Specimen Illumination: The light source illuminates the specimen on the stage.
- Objective Lens Magnification: The objective lens gathers light from the specimen and forms a real, inverted, and magnified image.
- Body Tube Transmission: This real image is then transmitted through the body tube. The precise length and alignment within the body tube are crucial for this transmission.
- Eyepiece Lens Magnification: The eyepiece lens further magnifies this image, creating a virtual image that the observer sees.
Maintaining Optical Alignment: A Delicate Balance
The body tube's rigid structure ensures the precise parallel alignment of the objective and eyepiece lenses. Even a slight misalignment can result in a distorted or blurry image. The manufacturing process requires high precision to ensure this alignment is maintained. Any damage or adjustment to the body tube should be performed by trained professionals to avoid compromising its functionality.
Body Tube Variations Across Microscope Types
The design and characteristics of the body tube vary depending on the type of microscope:
1. Compound Microscopes:
Compound microscopes use a body tube to connect the objective and eyepiece lenses. The length of the body tube is often standardized (e.g., 160mm), though variations exist. Many modern compound microscopes feature modular designs, allowing for greater flexibility in component configuration and customization.
2. Stereo Microscopes (Dissecting Microscopes):
Stereo microscopes, designed for low magnification observation of larger specimens, often have a different body tube configuration. The optical path may be split to create a three-dimensional image, with separate tubes leading to each eyepiece. The body tube in these microscopes often incorporates prisms or mirrors to achieve this stereoscopic vision.
3. Inverted Microscopes:
Inverted microscopes, used for observing living cells in culture dishes, have a body tube positioned below the stage. This design allows for easy access to the specimen, and the body tube's orientation is specifically adapted for this configuration. The optical pathway may incorporate more complex mirror systems to achieve the correct image orientation.
The Impact of Body Tube Length on Magnification
The length of the body tube directly influences the magnification of the microscope. While the magnification power is primarily determined by the objective and eyepiece lenses, the body tube's length plays a secondary, but important role in achieving the final magnification. This is especially critical in older microscope designs. Modern microscopes often incorporate infinity-corrected optics, where the body tube length is less critical to magnification.
Maintenance and Care of the Body Tube
Regular maintenance is essential to maintain the performance of the body tube and, consequently, the overall microscope.
- Avoid jarring or dropping the microscope: This can misalign the lenses and damage the delicate internal components.
- Handle with care: Avoid touching the internal surfaces of the body tube to prevent contamination or damage.
- Clean gently: If necessary, carefully clean the exterior of the body tube with a soft, lint-free cloth. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners.
- Professional servicing: If the microscope is not performing optimally or if the body tube is damaged, contact a qualified technician for servicing and repair.
Body Tube and Modern Microscope Advancements
The body tube remains a fundamental component even in modern microscopes with advanced features. However, several advancements influence its design and function:
- Infinity-Corrected Optics: Many modern microscopes utilize infinity-corrected optics, where the objective lens forms an image at infinity. This allows for greater flexibility in adding accessories (e.g., filters, cameras) in the optical path between the objective and eyepiece. The body tube's design in these microscopes is optimized for this infinite conjugate system.
- Modular Designs: Modular designs allow for greater flexibility in configuring the microscope to specific needs. The body tube in these microscopes acts as a connecting element for various components.
- Ergonomic Considerations: Modern microscope designs place a greater emphasis on ergonomics, considering the comfort and posture of the user. The body tube's position and design may be optimized for better viewing angles and reduced strain.
- Digital Integration: The integration of digital cameras and imaging systems requires modifications in the body tube design to accommodate the cameras and their connections.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero's Significance
The microscope body tube, despite being an often-overlooked component, plays a vital role in the performance and functionality of any microscope. Its critical function is to ensure the proper alignment and transmission of light, contributing significantly to the clarity and accuracy of the magnified image. Understanding its design, function, and variations across different microscope types is crucial for any user seeking to optimize the microscope's capabilities and appreciate the intricate engineering behind this remarkable tool. Proper care and maintenance of the body tube are essential to ensure its continued performance and longevity. By recognizing the body tube's significance, we can gain a more profound understanding of the power and precision of microscopy.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Super Bowls Do Packers Have
Apr 06, 2025
-
Darwin The Descent Of Man Summary
Apr 06, 2025
-
Great Famine Definition Ap World History
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is Rob Zombies Real Name
Apr 06, 2025
-
Did The Early Church Celebrate Easter
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Function Of Body Tube In Microscope . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.