Germany Takes Alsace-lorraine Region From France In The Franco-prussian War
Espiral
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
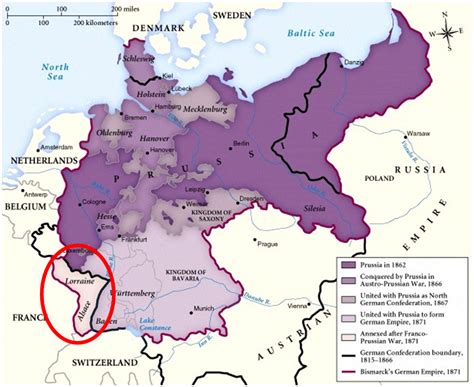
Table of Contents
Germany Takes Alsace-Lorraine: A Defining Moment of the Franco-Prussian War
The Franco-Prussian War, a brutal conflict fought between France and the newly unified German Empire in 1870-1871, irrevocably altered the political landscape of Europe. Central to this transformation was the annexation of Alsace-Lorraine by Germany, a territory that became a potent symbol of national humiliation for France and a source of enduring tension between the two nations for decades to come. This article will delve into the historical context, military events, and lasting consequences of Germany's seizure of Alsace-Lorraine, exploring the complex interplay of nationalism, power politics, and territorial ambition that shaped this pivotal moment in European history.
The Seeds of Conflict: Nationalism and Power Politics
The Franco-Prussian War wasn't a spontaneous eruption; it was the culmination of decades of simmering tensions between France and Prussia, fueled by burgeoning nationalism and a shifting balance of power in Europe. Prussia, under the masterful leadership of Otto von Bismarck, had skillfully orchestrated a series of political maneuvers to unify the German states under Prussian dominance. This unification, however, directly threatened France's position as the dominant continental power.
French anxieties about Prussian power
France, under Napoleon III, viewed the growing power of a unified Germany as a direct challenge to its hegemony. The spectre of a powerful neighbor on its eastern border fueled French anxieties. Furthermore, the French Empire harbored lingering resentment from previous conflicts, including the Napoleonic Wars. This historical baggage contributed to a climate of suspicion and hostility between the two nations.
Bismarck's masterful manipulation
Bismarck, a master strategist, expertly played upon French insecurities and vulnerabilities. He deliberately manipulated events to goad France into declaring war, ensuring that international opinion would largely favor Prussia and its allies. The Ems Dispatch, a carefully edited telegram concerning a diplomatic incident involving the Spanish throne, is a prime example of Bismarck’s manipulative tactics. This cleverly crafted telegram inflamed French public opinion and pushed Napoleon III towards a fateful decision to declare war.
The Military Campaign: A Prussian Triumph
The Prussian military machine, highly disciplined and technologically advanced, proved far superior to the French army. Several key factors contributed to the Prussian victory:
Superior Prussian military organization and technology
Prussia's military reforms, implemented under the guidance of Prussian military strategists like Helmuth von Moltke the Elder, had created a highly efficient and well-organized army. The use of railroads for rapid troop deployment and the adoption of breech-loading rifles, which had a much faster rate of fire than French rifles, gave the Prussian army a significant technological advantage.
The Battle of Sedan: A decisive turning point
The Battle of Sedan, fought in September 1870, proved to be a decisive turning point in the war. The French army, under the command of Napoleon III, was decisively defeated, leading to the capture of the emperor himself. This victory shattered French morale and effectively crippled the French war effort.
The Siege of Paris: A symbol of French defeat
The subsequent siege of Paris, which lasted for months, further underscored the overwhelming Prussian military superiority. The city's capture and the eventual surrender of the French forces marked the culmination of the Prussian triumph and paved the way for the harsh peace terms imposed on France.
The Annexation of Alsace-Lorraine: A Bitter Pill for France
The Treaty of Frankfurt, signed in May 1871, formally concluded the war and imposed stringent conditions on France. The most significant of these was the annexation of Alsace-Lorraine.
The strategic and symbolic importance of Alsace-Lorraine
Alsace-Lorraine, a region with a mixed population of French and German speakers, held considerable strategic and symbolic importance. Its strategic location bordering both France and Germany, along with its rich industrial resources, made it a highly desirable territory for Prussia. Moreover, the annexation served as a powerful symbol of German victory and French humiliation.
The impact on the Alsatian and Lorrainian populations
The annexation deeply affected the Alsatian and Lorrainian populations. While some welcomed the incorporation into the German Empire, many others, particularly those with strong French cultural and linguistic ties, fiercely resisted German rule. This resistance manifested itself in various forms, including cultural preservation efforts and sporadic acts of defiance. The population's loyalty remained deeply divided.
The lasting legacy of resentment
The annexation of Alsace-Lorraine left a deep and lasting scar on Franco-German relations. The loss of the territory became a potent symbol of national humiliation for France, fueling intense resentment and fostering a desire for revenge. This lingering resentment played a significant role in shaping the political climate in both countries for decades to come, even contributing to the tensions that led to World War I.
The Long-Term Consequences: A Century of Tension
The annexation of Alsace-Lorraine had far-reaching consequences that extended well beyond the immediate aftermath of the Franco-Prussian War:
The rise of German nationalism
The acquisition of Alsace-Lorraine bolstered German national pride and contributed to the rise of aggressive German nationalism. The territory became a symbol of German strength and success, reinforcing a sense of national identity and ambition among German citizens.
The fueling of French revanchism
Conversely, the loss of Alsace-Lorraine intensified French nationalism and fueled a sentiment known as revanchism, a desire to reclaim the lost territories. This sentiment would play a significant role in shaping French foreign policy in the years leading up to World War I. The desire to regain Alsace-Lorraine became a major motivating factor driving French diplomatic and military strategies.
The creation of a strategic flashpoint
Alsace-Lorraine became a persistent point of contention and a potential flashpoint for renewed conflict between France and Germany. The strategic location of the region, coupled with the unresolved sentiments on both sides, made it a vulnerable area ripe for future conflict. The intense rivalry created a situation where any perceived slight or aggression could easily escalate into open warfare.
The Return of Alsace-Lorraine: A Post-World War I Settlement
After the defeat of Germany in World War I, Alsace-Lorraine was returned to France. The Treaty of Versailles, which officially ended the war, restored the region to French control.
The symbolic importance of the return
The return of Alsace-Lorraine held immense symbolic significance for France. It marked not only the recovery of lost territory but also a symbolic affirmation of French national identity and a rejection of German dominance. The restoration of the region acted as a powerful symbol of French victory and national redemption.
The integration process after the return
The integration process, however, wasn't without challenges. The prolonged period of German rule had altered the region's social and political fabric, creating complexities in its reintegration into France. The process involved addressing issues of language, culture, and political alignment, requiring considerable effort and time to fully reestablish French identity in the region.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Conflict and Reconciliation
The annexation of Alsace-Lorraine by Germany during the Franco-Prussian War represents a pivotal moment in European history, shaping the geopolitical landscape and leaving a lasting legacy of conflict and reconciliation. The acquisition of the territory, while a triumph for Germany, deeply wounded French national pride and ignited decades of animosity. The ensuing tensions, fueled by nationalistic fervor and unresolved territorial disputes, played a critical role in the events that led to World War I. However, the eventual return of Alsace-Lorraine after World War I, while symbolic of French victory, also marked the beginning of a long process of reconciliation between France and Germany, a process that continues to this day. The story of Alsace-Lorraine serves as a stark reminder of the devastating consequences of unchecked nationalism and the enduring power of historical grievances.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Did Pat Garrett Kill Billy The Kid
Apr 02, 2025
-
Who Is The Unionist Party In Government
Apr 02, 2025
-
Why Do You Put A Christmas Tree Up
Apr 02, 2025
-
Aaron Rodgers Ever Won A Superbowl
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Many Acres Is Cincinnati Zoo
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Germany Takes Alsace-lorraine Region From France In The Franco-prussian War . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
