What Are The Resources Of India
Espiral
Apr 05, 2025 · 7 min read
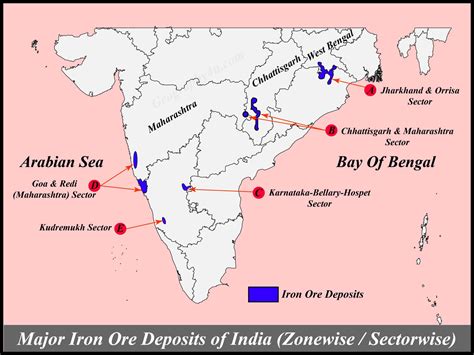
Table of Contents
What Are the Resources of India? A Comprehensive Overview
India, a land of diverse geography and vibrant culture, boasts a wealth of natural resources that have significantly contributed to its economic growth and development. Understanding these resources is crucial to comprehending India's past, present, and future trajectory. This comprehensive article delves into the various resources available in India, categorized for clarity and enhanced understanding. We'll explore their distribution, significance, and the challenges associated with their sustainable utilization.
I. Mineral Resources: The Foundation of Industry
India possesses a rich endowment of mineral resources, forming the bedrock of its burgeoning industrial sector. These resources are broadly categorized as metallic and non-metallic minerals.
A. Metallic Minerals: Fueling Industrial Growth
-
Iron Ore: India is one of the world's leading producers of iron ore, primarily found in states like Odisha, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and Karnataka. This vital raw material fuels the country's steel industry, a cornerstone of its infrastructure development. The high-grade hematite ore deposits significantly contribute to the global steel market. Challenges: Sustainable mining practices, addressing environmental concerns related to mining activities, and ensuring equitable distribution of benefits are key challenges.
-
Manganese Ore: Crucial for steel production and various other industrial applications, manganese ore is abundantly found in Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, and Karnataka. Its strategic importance necessitates careful management and responsible mining. Challenges: Similar to iron ore, sustainable mining and environmental protection are paramount concerns.
-
Bauxite: The primary ore of aluminum, bauxite is found in Odisha, Gujarat, Jharkhand, and Maharashtra. The aluminum industry is a crucial sector, contributing significantly to packaging, transportation, and construction. Challenges: Balancing the demand for bauxite with the need for environmental protection and responsible land use is a major concern.
-
Copper: India possesses copper deposits, albeit smaller compared to its iron ore reserves. States like Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Andhra Pradesh are significant copper-producing regions. Challenges: Meeting the increasing demand for copper while minimizing environmental impact requires strategic planning and investment in sustainable mining technologies.
-
Zinc and Lead: These vital metals, essential for various industrial and consumer applications, are found in Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh, and other states. Challenges: Optimizing extraction processes, managing waste, and ensuring responsible disposal are crucial aspects of sustainable zinc and lead mining.
-
Chromite: Used primarily in the production of stainless steel, chromite deposits are found in Odisha, Karnataka, and Maharashtra. Challenges: Balancing the demands of the steel industry with responsible mining practices and environmental considerations is crucial.
B. Non-Metallic Minerals: Supporting Diverse Industries
-
Coal: India's vast coal reserves, primarily located in Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, and Madhya Pradesh, are crucial for its energy sector and various industries. Coal remains a significant contributor to electricity generation, though efforts are underway to diversify the energy mix. Challenges: Reducing reliance on coal to mitigate environmental impacts and transitioning towards cleaner energy sources are major challenges.
-
Limestone: A vital component in cement manufacturing and various other industries, limestone is abundantly found across many states. Challenges: Sustainable quarrying practices and minimizing the environmental impact of limestone extraction are essential.
-
Phosphate Rock: Essential for fertilizer production, phosphate rock deposits are found in Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Gujarat. Meeting the growing agricultural demand for fertilizers while ensuring responsible mining is crucial. Challenges: Balancing agricultural needs with environmental concerns related to phosphate mining and fertilizer use.
II. Energy Resources: Powering the Nation
India's energy needs are substantial, and the country leverages a mix of resources to meet its demand.
A. Fossil Fuels: The Traditional Backbone
-
Coal: As mentioned earlier, coal remains a significant source of energy for power generation, despite the growing emphasis on renewable energy sources.
-
Petroleum and Natural Gas: While India imports a significant portion of its petroleum and natural gas needs, it also possesses domestic reserves, although production is not enough to meet the national demand completely. Exploration and extraction activities continue, with some success in offshore and onshore fields. Challenges: Reducing reliance on imports through increased domestic production and transitioning towards cleaner energy sources are crucial.
B. Renewable Energy: A Growing Sector
-
Solar Energy: India has immense potential for solar energy due to its abundant sunshine. Large-scale solar power plants are being developed across the country, significantly contributing to the renewable energy mix.
-
Wind Energy: Several states, particularly along coastal regions and in high-altitude areas, possess significant wind energy potential. Wind farms are being established to harness this clean energy source.
-
Hydropower: India's numerous rivers and abundant water resources provide a significant potential for hydropower generation. Large and small hydroelectric power plants contribute to the national electricity grid. Challenges: Environmental concerns related to dam construction and the impact on river ecosystems need careful consideration.
-
Biomass Energy: Agricultural residues and other organic materials can be utilized for biomass energy generation, providing a sustainable and decentralized energy source.
III. Water Resources: Life's Essence
India's water resources are diverse, encompassing rivers, lakes, groundwater, and rainwater. However, water scarcity is a growing concern, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions.
-
Rivers: The Indus, Ganga, Brahmaputra, and their tributaries are major river systems, crucial for irrigation, drinking water, and hydropower generation. However, pollution and unsustainable water management practices are posing significant challenges.
-
Groundwater: Groundwater is a vital source of drinking water and irrigation in many parts of the country. However, over-extraction and pollution are leading to depletion of groundwater resources in several areas.
-
Rainwater Harvesting: Rainwater harvesting techniques are increasingly being adopted to conserve rainwater and recharge groundwater resources. This is a crucial strategy for water management in regions prone to droughts.
IV. Land Resources: Agriculture and Beyond
India's land resources are crucial for agriculture, forestry, and other land uses.
-
Arable Land: A significant portion of India's land is arable, supporting a diverse range of crops. However, land degradation, soil erosion, and unsustainable agricultural practices are posing challenges.
-
Forests: India's forests are biodiversity hotspots, providing timber, non-timber forest products, and vital ecosystem services. However, deforestation and habitat loss are major concerns.
-
Other Land Uses: Land is also utilized for urban development, infrastructure projects, and other purposes. Sustainable land use planning is crucial to balance development with environmental protection.
V. Biological Resources: Biodiversity and Wealth
India's rich biodiversity is a valuable national asset.
-
Flora: India possesses a remarkable diversity of plant life, including numerous medicinal plants, timber trees, and other economically important species.
-
Fauna: India is home to a rich variety of animal species, including many endangered species. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect this biodiversity.
-
Fisheries: India's coastal regions and inland waterways support a thriving fisheries sector, providing a significant source of food and livelihood. Sustainable fishing practices are essential to prevent overfishing and depletion of fish stocks.
VI. Challenges and Opportunities
India's abundant resources present both challenges and opportunities. Sustainable management is crucial to ensure that these resources are utilized responsibly and equitably for the benefit of present and future generations.
-
Sustainable Resource Management: Adopting sustainable practices in mining, agriculture, forestry, and energy production is crucial to minimize environmental damage and ensure long-term resource availability.
-
Technological Advancements: Investing in research and development to improve resource extraction techniques, develop cleaner energy sources, and enhance resource efficiency is essential.
-
Equitable Distribution: Ensuring equitable access to resources and the benefits derived from them is crucial for social justice and economic development.
-
Environmental Protection: Protecting biodiversity, mitigating pollution, and preventing land degradation are crucial for preserving the ecological integrity of India's natural environment.
-
Policy and Governance: Effective policy frameworks and robust governance structures are needed to ensure the sustainable and responsible management of India's resources.
Conclusion: A Path Towards Sustainable Development
India's vast and diverse natural resources have been instrumental in its growth and development. However, the sustainable utilization of these resources is paramount for ensuring the country's continued progress and prosperity. By embracing sustainable practices, investing in technological advancements, and implementing effective policies, India can harness its natural wealth to achieve sustainable development and ensure a prosperous future for its people. The journey requires a holistic approach, integrating economic growth with environmental protection and social equity. This requires not only governmental intervention but also active participation from citizens and businesses alike, fostering a culture of responsibility and sustainability in resource management. Only then can India truly unlock the full potential of its rich natural heritage.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Difference Between An Alpaca And Llama
Apr 05, 2025
-
What Is The Value Of A Shilling
Apr 05, 2025
-
Fernando Botero Death Of Pablo Escobar
Apr 05, 2025
-
What Are The New Signs Of The Zodiac
Apr 05, 2025
-
The Biography Of Mary The Mother Of Jesus
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Resources Of India . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.