What Is A Pile In Construction
Espiral
Apr 02, 2025 · 6 min read
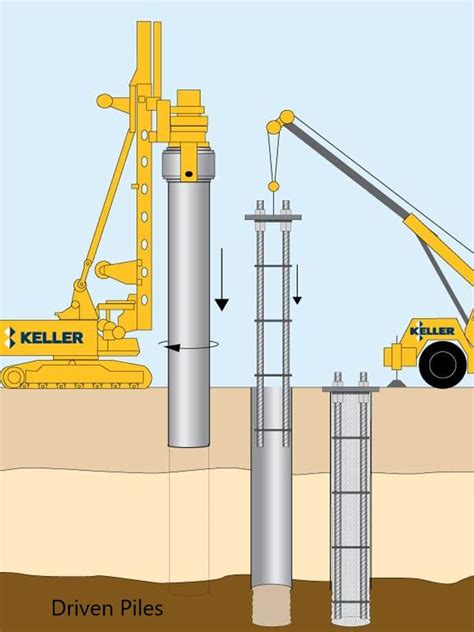
Table of Contents
What is a Pile in Construction? A Comprehensive Guide
A pile, in the context of construction, is a long, slender structural element driven or bored into the ground to provide a stable foundation for buildings, bridges, or other structures. Piles transfer structural loads from the superstructure (the building itself) down to a suitable soil stratum or rock, overcoming issues with weak or unstable soil conditions. Understanding piles is crucial for engineers, architects, and anyone involved in large-scale construction projects. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types, applications, and considerations surrounding pile foundations.
Types of Piles: A Deep Dive
Piles are categorized based on their material, installation method, and load-bearing mechanism. Let's explore some of the most common types:
1. Based on Material:
-
Timber Piles: These were historically prevalent, using durable hardwoods like oak or pine. They are relatively inexpensive but susceptible to decay and insect infestation, limiting their lifespan and applications. Their use is now largely restricted to situations where they are protected from the elements or have a very short service life.
-
Concrete Piles: These are incredibly versatile and the most commonly used type today. They can be precast (manufactured off-site and driven or placed into position) or cast-in-situ (poured directly into the ground). Precast piles offer consistent quality and faster installation, while cast-in-situ piles adapt well to complex site conditions.
-
Precast Concrete Piles: These are available in various shapes (e.g., square, rectangular, circular) and lengths, offering flexibility in design and load capacity.
-
Cast-in-Situ Concrete Piles: These offer greater flexibility in terms of pile length and shape, allowing for adaptation to varying ground conditions. Techniques include bored piles (using a drill), CFA (continuous flight auger) piles, and displacement piles.
-
-
Steel Piles: Steel piles are strong, durable, and reusable, making them suitable for projects requiring high load-bearing capacity and repeated driving. They are often used in challenging soil conditions, such as dense gravel or rock. However, they are susceptible to corrosion, requiring protective coatings.
2. Based on Installation Method:
-
Driven Piles: These are hammered or vibrated into the ground using specialized equipment like pile hammers or vibratory hammers. This method is efficient for precast concrete or steel piles in suitable soil conditions.
-
Bored Piles: These are created by drilling a hole in the ground and then filling it with concrete. This method is ideal for challenging soil conditions where driving piles might be difficult or cause damage to surrounding structures. They provide excellent load-bearing capabilities and are suitable for large-diameter piles.
-
Auger Piles: These utilize a continuous flight auger to create the hole and simultaneously deposit concrete, offering an efficient and clean installation method. They are suitable for various soil types and are often used in less restricted spaces.
3. Based on Load-Bearing Mechanism:
-
End-Bearing Piles: These transfer loads to a strong, load-bearing stratum (like bedrock) at their base. They are ideal when a suitable bearing layer is located at a reasonable depth.
-
Friction Piles: These rely on the friction between the pile's surface and the surrounding soil to support the load. They are commonly used in cohesive soils (like clay) where a suitable bearing stratum is not readily available.
-
Combined End-Bearing and Friction Piles: Many piles act as a combination of both end-bearing and friction piles, transferring loads through both mechanisms. This is a common and effective approach for many site conditions.
Factors Affecting Pile Selection
The choice of pile type depends on several crucial factors:
-
Soil Conditions: The type of soil, its density, strength, and groundwater conditions significantly influence pile selection. Weak or unstable soil necessitates piles with higher load-bearing capacity and appropriate installation methods. Detailed geotechnical investigations are essential to determine the suitable pile type.
-
Load Requirements: The weight and type of structure determine the required load-bearing capacity of the piles. Heavier structures or those subjected to significant dynamic loads (e.g., bridges, machinery) necessitate piles with greater strength.
-
Environmental Considerations: Factors like proximity to existing structures, underground utilities, and environmental regulations play a crucial role in pile selection and installation methods. Minimizing environmental impact is increasingly important.
-
Project Budget and Time Constraints: Different pile types have varying costs and installation times. Balancing cost-effectiveness with project timelines is critical.
-
Accessibility: Site accessibility can impact the choice of pile installation method. Confined spaces may necessitate smaller-diameter piles or specialized installation techniques.
Installation Process: A Step-by-Step Overview
The pile installation process can vary depending on the pile type and site conditions. However, it generally involves the following steps:
-
Site Investigation and Geotechnical Analysis: This crucial initial step involves conducting soil tests and analyzing the ground conditions to determine the optimal pile type, length, and spacing.
-
Pile Design and Specifications: Based on the site investigation, engineers design the piles to meet the required load-bearing capacity and safety standards.
-
Equipment Mobilization: Specialized equipment is mobilized to the site, including pile hammers, vibratory hammers, drilling rigs, or other relevant machinery.
-
Pile Installation: The piles are driven, bored, or augered into the ground according to the chosen method. Careful monitoring ensures the piles are installed to the specified depth and alignment.
-
Quality Control and Testing: Various tests, including pile integrity testing (e.g., dynamic load testing) and concrete testing, are performed to verify the pile's load-bearing capacity and quality.
-
Pile Capping: Once the piles are installed, a pile cap (a reinforced concrete slab) is placed on top to distribute the load from the superstructure evenly across the piles.
-
Superstructure Construction: After the pile cap is completed, the construction of the superstructure can begin.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Pile Foundations
Advantages:
- Increased Load-Bearing Capacity: Piles can support heavy loads on weak or unstable soils.
- Deep Foundation: They allow construction on sites with inadequate shallow soil conditions.
- Stability and Settlement Control: They offer increased stability and control over foundation settlement.
- Suitability for Various Soil Types: They can be adapted for use in a variety of soil conditions.
- Reduced Settlement: They significantly reduce the risk of excessive foundation settlement.
Disadvantages:
- High Initial Cost: Pile foundations typically have a higher initial cost compared to other foundation types.
- Complex Installation: Installation can be complex and time-consuming, especially in challenging conditions.
- Noise and Vibration: Driving piles can generate noise and vibration, which may need to be mitigated.
- Potential for Environmental Impact: Improper installation can lead to ground disturbance and environmental impacts.
- Difficult Inspection: Inspecting the integrity of piles after installation can be challenging.
Common Applications of Pile Foundations
Pile foundations are used in a wide variety of construction projects, including:
- High-rise Buildings: Providing a stable foundation for tall structures in areas with weak soil.
- Bridges and Viaducts: Supporting the weight and dynamic loads of bridges and elevated roadways.
- Offshore Structures: Used in the construction of offshore platforms and wind turbines.
- Retaining Walls: Providing support for large retaining walls and embankments.
- Industrial Structures: Supporting heavy machinery and industrial facilities.
- Seismic Zones: Increasing stability in areas prone to earthquakes.
Conclusion: The Importance of Pile Foundations
Pile foundations are essential structural elements in various construction projects, particularly those involving challenging soil conditions or heavy loads. Selecting the appropriate pile type and installation method is crucial for ensuring the structural integrity and longevity of the structure. Careful planning, detailed geotechnical investigations, and adherence to strict construction practices are essential for successful pile foundation projects. Understanding the various aspects discussed in this guide can contribute significantly to informed decision-making in any project involving pile foundations. Furthermore, continuous research and technological advancements in pile foundation techniques continue to improve efficiency, safety, and sustainability in construction.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Tall Are The Nba Basketball Hoops
Apr 03, 2025
-
Where Is The Strait Of Juan De Fuca
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Were Some Of Andrew Jacksons Accomplishments
Apr 03, 2025
-
Who Are The Announcers On Monday Night Football
Apr 03, 2025
-
Is The Big Dipper Part Of Orions Belt
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Pile In Construction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
