What Is Argon On The Periodic Table
Espiral
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
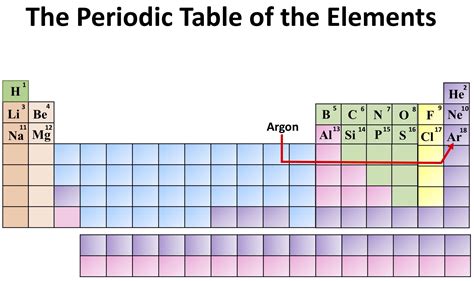
Table of Contents
- What Is Argon On The Periodic Table
- Table of Contents
- What is Argon on the Periodic Table? A Deep Dive into the Inert Noble Gas
- Argon's Atomic Structure and Properties
- The Discovery of Argon: A Story of Scientific Inquiry
- Argon Production: From Air to Industrial Applications
- The Diverse Applications of Argon: A Versatile Element
- 1. Welding and Metallurgy
- 2. Lighting and Illumination
- 3. Scientific and Medical Applications
- 4. Electronics and Semiconductor Industry
- 5. Food Packaging and Preservation
- 6. Other Applications
- Environmental Considerations and Safety
- Conclusion: Argon's Enduring Significance
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What is Argon on the Periodic Table? A Deep Dive into the Inert Noble Gas
Argon, represented by the symbol Ar and atomic number 18, holds a significant place on the periodic table as a noble gas. Understanding its properties, uses, and overall significance requires delving into its atomic structure, reactivity, and widespread applications across various industries. This comprehensive guide will explore argon in detail, covering its discovery, characteristics, production, and its crucial roles in diverse fields.
Argon's Atomic Structure and Properties
Argon, unlike many other elements, exists as a monatomic gas, meaning its atoms are not bonded together to form molecules. This is a direct consequence of its electron configuration, a defining feature of its noble gas classification. Its atomic number of 18 signifies that it possesses 18 protons and, in its neutral state, 18 electrons. These electrons are arranged in three electron shells: 2, 8, and 8. This stable octet configuration in the outermost shell is the key to argon's inertness.
Key Properties of Argon:
- Inertness: Argon's filled outermost electron shell makes it exceptionally unreactive. It rarely forms chemical compounds, hence its classification as a noble gas. This inertness is crucial for many of its applications.
- Gas at Room Temperature: Under standard conditions, argon is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas.
- Low Density: It's less dense than air, making it suitable for certain applications where buoyancy is a factor.
- Poor Conductor of Heat and Electricity: Its electronic structure contributes to its low conductivity, making it valuable as an insulator.
- Non-toxic: Argon's inertness and lack of toxicity make it safe to handle and use in various settings.
- Abundance: Argon is relatively abundant in the Earth's atmosphere, constituting about 0.934% by volume. This ready availability makes it economically viable for various industrial uses.
The Discovery of Argon: A Story of Scientific Inquiry
The discovery of argon marked a significant turning point in the understanding of noble gases. Unlike many elements discovered through chemical reactions, argon's discovery relied on meticulous observation and deduction. Lord Rayleigh and Sir William Ramsay are credited with its discovery in 1894. They noticed a discrepancy between the density of nitrogen extracted from air and nitrogen produced from chemical compounds. This difference led them to investigate further, eventually isolating a new gas – argon. This discovery expanded the periodic table and challenged existing chemical theories, paving the way for the identification of other noble gases.
Argon Production: From Air to Industrial Applications
Argon's abundance in the atmosphere is the foundation of its large-scale production. The primary method for extracting argon involves the fractional distillation of liquid air. This process takes advantage of the slight differences in boiling points of the various components of air. Air is first liquefied under high pressure and then carefully fractionated, separating argon from other gases like nitrogen and oxygen.
The Fractional Distillation Process:
The process involves several steps:
- Air Compression and Purification: Air is compressed and purified to remove impurities like carbon dioxide and water vapor.
- Liquefaction: The purified air is then cooled and compressed until it liquefies.
- Fractional Distillation: The liquid air is carefully warmed in a fractional distillation column. Different components vaporize at different temperatures, allowing for their separation. Argon, with its intermediate boiling point, is collected separately.
- Purification: The extracted argon is further purified to ensure high purity for various applications.
This industrial process allows for the production of large quantities of argon, meeting the demands of various sectors.
The Diverse Applications of Argon: A Versatile Element
Argon's unique properties make it an indispensable element in a wide range of applications. Its inertness, low density, and non-reactivity are crucial for its various uses. Here are some notable examples:
1. Welding and Metallurgy
Argon's inertness is exceptionally valuable in welding processes. It acts as a shielding gas, preventing the molten metal from reacting with atmospheric oxygen and nitrogen, which can lead to defects and reduce the weld's strength. Argon shielding gas ensures a clean and high-quality weld. Furthermore, it's used in other metallurgical processes, where preventing oxidation is crucial.
2. Lighting and Illumination
Argon plays a vital role in various lighting technologies. It is used as a fill gas in incandescent light bulbs to prevent oxidation of the filament, thereby prolonging bulb life. Additionally, argon is used in fluorescent lighting, acting as a buffer gas to improve lamp efficiency.
3. Scientific and Medical Applications
Argon's inertness finds use in various scientific instruments and medical applications. It is used as a carrier gas in chromatography and other analytical techniques. In medicine, argon is sometimes used in certain laser treatments.
4. Electronics and Semiconductor Industry
The semiconductor industry utilizes argon as a purge gas to remove oxygen and moisture during the manufacturing of sensitive electronic components. Its inertness is crucial in preventing oxidation and contamination, safeguarding the integrity of these delicate devices.
5. Food Packaging and Preservation
In the food industry, argon is sometimes employed as a packaging gas. It creates an inert atmosphere, preventing spoilage and oxidation, thereby extending the shelf life of packaged food products. This prevents the growth of oxygen-dependent microorganisms.
6. Other Applications
Beyond these key applications, argon finds use in other areas such as:
- Fire suppression systems: Argon's inertness makes it a suitable alternative to halon in fire extinguishing systems.
- Cryosurgery: In some medical procedures, argon is used for its cryogenic properties.
- Tyre inflation: Some high-performance tyres utilize argon for improved thermal stability.
Environmental Considerations and Safety
While argon is generally considered inert and non-toxic, certain safety precautions should be observed when handling it. As it's heavier than air, it can displace oxygen in confined spaces, posing a potential asphyxiation risk. Proper ventilation and safety measures are crucial when working with large quantities of argon.
Furthermore, the production of argon, involving energy-intensive air liquefaction, has some environmental implications. However, its overall environmental impact is significantly less compared to other industrial processes. The industry continuously seeks ways to improve efficiency and minimize the environmental footprint of argon production.
Conclusion: Argon's Enduring Significance
Argon, a seemingly unremarkable noble gas, plays a vital and often unseen role in numerous aspects of modern life. From welding and electronics to lighting and food preservation, its unique properties have made it an indispensable element across diverse industries. Its inertness, abundance, and relatively simple production process contribute to its widespread applications. As technology continues to evolve, argon's significance is likely to remain prominent, further highlighting its crucial role in our modern world. Further research into its properties and potential applications continues to unfold, promising even more innovative uses in the future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Do They Call It Saltwater Taffy
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Was St Peter The Patron Saint Of
Apr 01, 2025
-
5 Facts About The Independence Of Mexico
Apr 01, 2025
-
Primates Teeth Are Unique Because They Are
Apr 01, 2025
-
Is Laverne Cox A Man Or A Woman
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Argon On The Periodic Table . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
