Which Sea Separates Europe From Africa
Espiral
Apr 03, 2025 · 5 min read
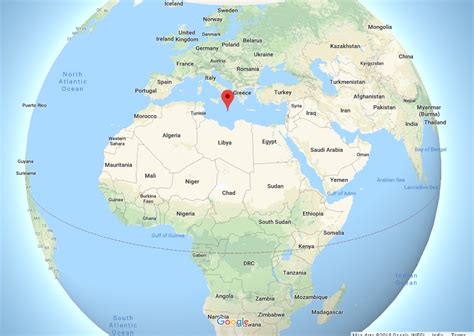
Table of Contents
Which Sea Separates Europe from Africa? A Deep Dive into the Mediterranean
The simple answer is the Mediterranean Sea. However, understanding the geographical relationship between Europe and Africa requires delving deeper than a single sentence. This article will explore the Mediterranean Sea, its historical significance, its diverse ecosystem, and the geopolitical factors influencing its importance, all while addressing the question of what separates these two continents in detail.
The Mediterranean Sea: A Geographical Overview
The Mediterranean Sea is a vast body of water, approximately 2,500,000 square kilometers (965,000 sq mi) in area, connecting Europe, Africa, and Asia. It's a nearly landlocked sea, with only a narrow connection to the Atlantic Ocean through the Strait of Gibraltar and a smaller connection to the Black Sea via the Dardanelles, Sea of Marmara, and the Bosporus. This relative isolation has resulted in a unique and diverse marine environment.
Key Geographical Features:
- The Strait of Gibraltar: This narrow passage between Spain and Morocco is the crucial link between the Mediterranean and the Atlantic Ocean. Its strategic importance throughout history cannot be overstated.
- The Aegean Sea: A sub-basin of the Mediterranean Sea, separating Greece from Turkey, studded with thousands of islands.
- The Adriatic Sea: Separates Italy from the Balkan Peninsula.
- The Ionian Sea: Situated south of the Adriatic Sea, it lies between Italy, Greece, and Albania.
- The Tyrrhenian Sea: Located west of Italy, it's known for its volcanic activity and stunning islands like Sicily.
- The Balearic Sea: A western sub-basin located east of Spain.
More Than Just Water: The Mediterranean's Historical Significance
The Mediterranean Sea has played an unparalleled role in shaping human civilization. For millennia, it served as a vital conduit for trade, migration, and cultural exchange. Its shores cradle the birthplaces of numerous ancient civilizations, including those of Ancient Greece, Rome, and Carthage.
A Cradle of Civilizations:
- Ancient Greece: The Aegean Sea played a pivotal role in the rise of ancient Greek city-states, facilitating trade and enabling the spread of Hellenic culture throughout the Mediterranean.
- The Roman Empire: The Mediterranean, known to the Romans as Mare Nostrum ("Our Sea"), became the central artery of their vast empire, uniting diverse peoples and cultures under Roman rule. Seaborne trade flourished, spreading Roman influence and enabling efficient administration of the empire.
- The Ottoman Empire: For centuries, the Ottoman Empire controlled significant portions of the Mediterranean coastline, influencing trade routes and wielding considerable political power.
The Mediterranean Sea also bore witness to countless conflicts and power struggles, shaping the political landscape of Europe, Africa, and the Middle East. Its strategic location made it a focal point for naval battles and territorial disputes throughout history, even into the modern era.
The Mediterranean Ecosystem: Biodiversity Under Pressure
The Mediterranean Sea is renowned for its rich biodiversity. Its unique blend of temperate and subtropical climates creates a haven for a wide array of marine life.
Unique Flora and Fauna:
- Endemic Species: The Mediterranean harbors a high number of endemic species, meaning they are found nowhere else on Earth. These species are particularly vulnerable to environmental changes.
- Coral Reefs: While not as extensive as in tropical regions, Mediterranean coral reefs are vital ecosystems, providing habitat for numerous fish and invertebrate species.
- Marine Mammals: Dolphins, whales, and seals inhabit the Mediterranean Sea, facing threats from pollution and habitat destruction.
- Sea Turtles: Several species of sea turtles, including loggerheads and green turtles, use the Mediterranean for nesting and feeding grounds.
Unfortunately, the Mediterranean ecosystem is facing considerable pressure from human activities. Pollution from industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, and plastic waste poses a significant threat. Overfishing depletes fish stocks, and coastal development destroys crucial habitats. Climate change further exacerbates these challenges, impacting water temperature, sea level, and the overall health of the marine environment.
Geopolitical Importance of the Mediterranean Sea: A Modern Perspective
The strategic importance of the Mediterranean Sea persists in the 21st century. It remains a crucial route for global shipping, connecting Europe with Asia and Africa. Energy resources, including oil and gas pipelines, traverse the seabed, highlighting the region's economic importance.
Modern Challenges:
- Migration: The Mediterranean has become a major route for migrants and refugees seeking to reach Europe from Africa and the Middle East, presenting significant humanitarian and political challenges.
- Security: The region faces security threats, including piracy, terrorism, and conflicts in neighboring countries. The sea's strategic location makes it a vital area for naval patrols and international cooperation.
- Environmental Protection: International collaboration is vital to address the escalating environmental challenges facing the Mediterranean Sea. Efforts to reduce pollution, protect biodiversity, and mitigate the effects of climate change are crucial for the long-term sustainability of this vital ecosystem.
Beyond the Simple Answer: A Deeper Understanding
While the Mediterranean Sea is the straightforward answer to the question of what separates Europe from Africa, it's crucial to appreciate the complexity of this geographical and historical relationship. The sea itself isn't simply a geographical boundary; it's a dynamic environment that has shaped civilizations, driven trade, and played a decisive role in shaping the geopolitical landscape of the world. Its future is intricately linked to the future of the countries that border it, emphasizing the importance of international cooperation in managing its resources, protecting its environment, and ensuring its long-term sustainability for generations to come. The Mediterranean is far more than just a body of water; it's a living testament to the interconnectedness of cultures, history, and the environment. Understanding its significance requires a comprehensive understanding of its geography, history, ecology, and geopolitical importance. This deeper understanding moves us beyond a simple answer and into the rich tapestry of human and natural history that defines this vital region.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Is A Government Run By Religious Leaders
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Many Days After Resurrection Did Jesus Ascend
Apr 04, 2025
-
Will Potter Green Is The New Red
Apr 04, 2025
-
Where Is Washington Dc On The United States Map
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Overall Reaction Formula For Photosynthesis
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Sea Separates Europe From Africa . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
