Panama Canal Joins Which Two Oceans
Espiral
Mar 28, 2025 · 7 min read
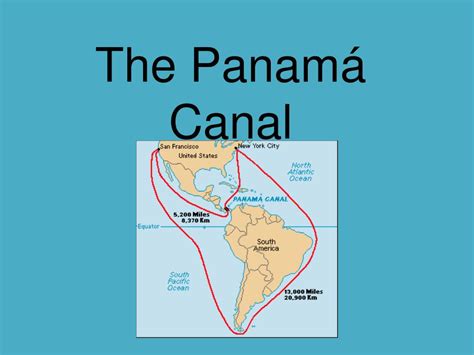
Table of Contents
Panama Canal: Joining the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans – A Marvel of Engineering and Global Trade
The Panama Canal, a marvel of engineering and a crucial artery of global trade, connects the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. This seemingly simple statement belies the immense complexity and historical significance of this waterway, which has profoundly impacted global commerce, geopolitics, and the environment for over a century. This article delves deep into the canal's history, its engineering marvels, its economic impact, and its enduring influence on the world.
A Geographical Bridge: Connecting Two Oceans
The Isthmus of Panama, a narrow strip of land connecting North and South America, has long been recognized as a potential shortcut between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Before the canal's construction, ships had to undertake a perilous and time-consuming journey around the southern tip of South America, a voyage known as the Cape Horn route. This arduous journey added weeks, if not months, to travel time and significantly increased costs. The creation of the Panama Canal drastically reduced this travel time, making it a pivotal link in global trade routes. The canal directly joins the Atlantic Ocean (specifically the Caribbean Sea) and the Pacific Ocean.
The Strategic Importance of the Canal's Location
The geographical location of the Panama Canal is not merely fortuitous; it's strategically paramount. Its position on the Isthmus of Panama allows ships to bypass a significant portion of their journey, saving substantial time, fuel, and costs. This strategic location has made Panama a crucial player in global geopolitics, influencing trade relationships and power dynamics for decades. The canal's location also plays a significant role in shaping global supply chains, affecting everything from the price of consumer goods to the efficiency of international trade.
The History of the Panama Canal: A Story of Perseverance and Challenges
The idea of a trans-isthmian canal dates back to the 16th century, but it wasn't until the late 19th and early 20th centuries that serious attempts at construction were made. The French, under the leadership of Ferdinand de Lesseps, who had successfully built the Suez Canal, initially undertook the project. However, they faced immense challenges, including:
- Disease: Yellow fever and malaria, rampant in the tropical climate of Panama, decimated the French workforce. Thousands of workers perished, halting the project.
- Engineering Difficulties: The terrain proved far more challenging than anticipated, with unstable ground and unpredictable rainfall.
- Financial Problems: The project significantly overran its budget, leading to financial ruin.
The United States eventually took over the project in 1904, employing innovative engineering solutions and stringent health measures to combat disease. They implemented a system of locks, allowing ships to navigate the elevation changes between the two oceans, and employed modern engineering techniques, including massive excavation using steam shovels and dredges. The American effort, though still fraught with challenges, ultimately led to the successful completion of the Panama Canal in 1914.
The Legacy of the French Effort
While the French ultimately failed to complete the canal, their efforts laid a crucial foundation. They conducted extensive surveys and geological studies, providing invaluable data for the subsequent American effort. Their experience, though costly in terms of human lives and financial resources, highlighted the enormous challenges involved and informed the strategies adopted by the Americans. The French failure serves as a cautionary tale of underestimating the scale and complexity of such a vast undertaking.
The Engineering Marvel of Locks and Waterways
The Panama Canal is not simply a dug-out trench; it's a complex system of locks, channels, and artificial lakes. The Gatún Lake, created by damming the Chagres River, forms a significant portion of the canal's waterway, reducing the length and the overall engineering challenges. The locks, a series of water-filled chambers, raise and lower ships to overcome the significant elevation difference between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. This ingenious system of locks allows ships of various sizes to traverse the canal safely and efficiently.
The Operation of the Locks: A Precise and Synchronized Process
The operation of the Panama Canal locks is a marvel of engineering and precise coordination. Water is carefully controlled to raise and lower ships through the locks, a process that involves the meticulous manipulation of massive gates and valves. The entire operation is closely monitored and controlled by skilled engineers and operators, ensuring the safe and efficient passage of ships through the canal. The technology and systems employed are constantly updated to improve efficiency and safety.
The Economic Impact of the Panama Canal: A Global Trade Hub
The Panama Canal's economic impact is immeasurable. It significantly reduces shipping times and costs, impacting global trade and supply chains in profound ways. It facilitates the transport of billions of dollars worth of goods annually, making it a critical artery for international commerce. The Canal's influence extends far beyond just shipping costs; it shapes global trade routes, affects the prices of goods, and even influences political relations between countries.
The Canal's Influence on Global Supply Chains
The Panama Canal's influence on global supply chains is immense. By shortening shipping routes, the canal has made it faster and cheaper to transport goods between the East and West coasts of the Americas and between Asia and Europe. This has facilitated the growth of global trade and has profoundly impacted industries ranging from agriculture and manufacturing to technology and consumer goods. The impact on consumer prices is considerable, as shorter shipping routes can help to keep the cost of goods down.
The Environmental Impact of the Panama Canal: Balancing Progress and Preservation
The construction and operation of the Panama Canal have had significant environmental impacts. The creation of Gatún Lake led to the flooding of vast areas of land, affecting local ecosystems and biodiversity. The increased shipping traffic through the canal also raises concerns about potential water pollution and the introduction of invasive species. However, Panama has implemented various environmental mitigation measures to reduce the canal's ecological footprint.
Efforts Towards Sustainability and Conservation
Panama is committed to ensuring the sustainable operation of the Panama Canal. They have implemented various measures to minimize environmental impact, including stricter regulations on ship emissions, the implementation of conservation programs to protect biodiversity, and ongoing research to study and mitigate the environmental impacts of the canal. The balance between economic progress and environmental protection remains a crucial challenge for Panama and the global community.
The Panama Canal Today and into the Future: Expansion and Ongoing Relevance
The Panama Canal continues to play a vital role in global trade, and ongoing expansions aim to further increase its capacity and efficiency. The recent expansion project, completed in 2016, significantly widened and deepened the canal, allowing the passage of larger "New Panamax" vessels. This expansion has increased the canal's capacity and has further solidified its position as a key player in global maritime trade. However, challenges remain, including the need for continued investment in infrastructure, adapting to changing global trade patterns, and ensuring the canal's long-term sustainability.
Challenges and Opportunities for the Future
The Panama Canal faces several challenges in the coming decades. These include increased competition from other shipping routes, the need for ongoing maintenance and modernization of infrastructure, and the need to address potential environmental concerns. However, the Canal also presents numerous opportunities, including further expansion, technological advancements, and the continued optimization of its operations to enhance efficiency and sustainability.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Innovation and Global Significance
The Panama Canal stands as a testament to human ingenuity, perseverance, and the transformative power of infrastructure. Its construction was a monumental undertaking that overcame significant obstacles and reshaped global trade patterns. It continues to be a critical artery for global commerce, impacting economies worldwide and shaping global supply chains. The canal's story is one of overcoming challenges, adapting to change, and the enduring importance of connecting the world through efficient and innovative infrastructure. The canal’s joining of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans is not just a geographical fact; it's a pivotal moment in global history, a symbol of human ambition and a cornerstone of modern global trade. The canal’s legacy extends far beyond its physical presence; it represents a profound shift in global connectivity and continues to influence the world in ways both seen and unseen.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Germany Takes Alsace Lorraine Region From France In The Franco Prussian War
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Is St John The Evangelist Known For
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Is Happening On October 3
Mar 31, 2025
-
When Does War Of The Worlds Take Place
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Many Dominoes Are In A Game
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Panama Canal Joins Which Two Oceans . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
